
Greenifying the Automotive Industry: The Sustainability of Electric Vehicles

Unless you’ve been living under a rock, you are probably aware of the ongoing global warming crisis. Harmful carbon emissions play a big part in worsening this environmental issue and according to a 2019 report: the transportation sector causes about 24% of these hazardous CO2 emissions worldwide. This is where electric cars come in. They release little to no emissions while you’re on the road as compared to fuel powered cars and pretty soon, these cars may prove to be game-changers for our planet. That sounds too good to be true, right? Well that’s because it is, as there are still some issues with EVs such as unsustainable battery production or the lack of proper infrastructure.
How Do Electric Vehicles Work?
The first electric car was introduced by Sibrandus Stratingh in the early 19th century yet combustion engines remained the dominant choice for more than a century. With growing awareness on environmental issues, more and more people have started opting for electric cars – but a few obstacles still stand in the way.
Electric cars use the electricity stored in rechargeable batteries to run their motors and emit fewer tailpipe emissions while running. So they use electricity instead of fossil fuels – but what if the electricity in question itself is produced by burning fuels? It completely eradicates the environmental benefits of owning an electric vehicle. Therefore, all EV owners should ensure that the electricity that they’re using has been produced by renewable or sustainable resources such as wind, solar, biofuels or other.
The power inside these batteries can only last so long so they need to be recharged – just as conventional cars need to be refueled. However unlike gas stations, these charging points are not as frequent. Europe, France, Germany and the Netherlands lead with 20,000-40,000 charging stations each. Whereas others like Romania, Greece and Estonia have merely 0-500 each.
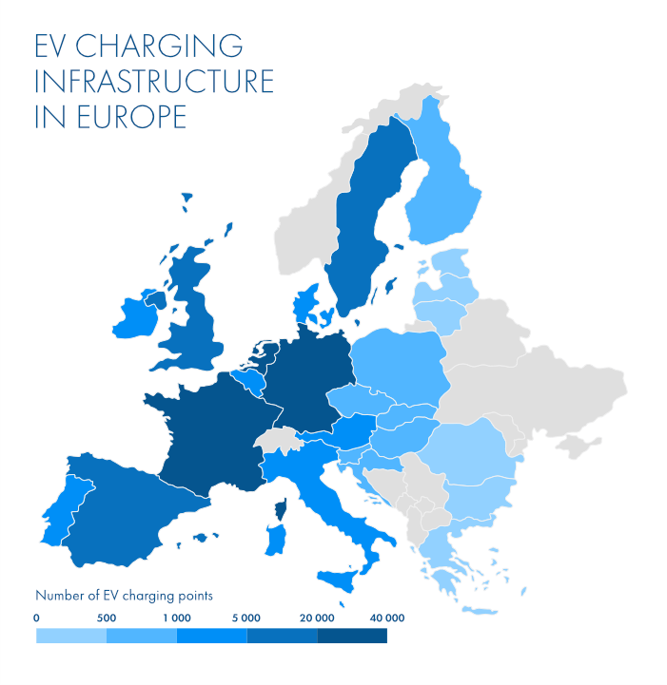
Source: 2019 in the automotive industry
In Europe, 2.8% of the vehicles registered by mid-2019 were electric, this could be caused by the lack of the right infrastructure. To further encourage the sales of EVs, more charging stations should be opened up, especially along the main highways. Currently there are approximately 185,000 points across the European Union whereas Transport and Environment (T&E) estimate there should be 3 million stations by 2030 to cater to the rising amount of EVs.
Meanwhile, the environmentally conscious need not be disheartened. Many major auto companies are working on a solution. In 2019, Tesla CEO Elon Musk announced production of a 1-million-mile battery, which would make the need for a recharge less frequent. The 400 and growing Supercharger stations in Europe set you on your way in 30 minutes. By 2020, Ionity plans to add its own 400 charging stations in EU with an average of 6 charging points each.
Electric Batteries: Harmful or Beneficial?
Recent studies present a troubling perspective on EV batteries – they might not be as beneficial to our environment after all.
Lithium, cobalt, manganese and other REE (rare earth elements) are often excruciatingly mined to make batteries for EVs. Thus, it takes almost twice the energy to make an electric car than a conventional one. Mining for these materials also strips the Earth of its natural resources and pollutes the land. Due to these disadvantages, auto giants such as Panasonic and Tesla are consciously trying to reduce the use of cobalt in their batteries as they have with the Model 3’s 2170 batteries.
Moreover, the production process for the EVs and their batteries releases a lot of emissions, which makes people wonder if it’s really helping our environment to go electric. Nonetheless, it is important to note the low amount of emissions they cause while on the road and it’s really a matter of whether or not this offsets the amount of CO2 released during production. According to a report by the EEA, electric cars need to be utilized to the maximum mileage to really make a difference – say more than 150,000 km.
Electric Vehicles and Their Rising Popularity
In addition to their sustainability, electric cars also have a lower running cost which compensates for the initial high costs. In Europe the average price for electric cars is $34,000. Auto companies such as Tesla are working on making EVs that are even more affordable such as the Model 3.
The advantages and disadvantages can be argued about all day, but statistics show that electric vehicles may soon replace fuel cars on the road. In 2018, the global stock for electric cars rose to 5.12 million. By early 2019, 5.6 million electric cars were on the road worldwide – a 64% increase whereas the sales of fossil fuel cars fell by 4.7% since 2018.These numbers can’t be denied. Electric vehicles have developed a lot over the last few years and are constantly being improved. In 2019, Volvo announced that all new models they design will be solely electric or hybrid vehicles. Jaguar is expected to follow suit in 2020.
All this makes the situation look promising for electric vehicles and it can be hoped that they’ll be even more beneficial and sustainable for our planet in the near future.



steve
this was extremly informative