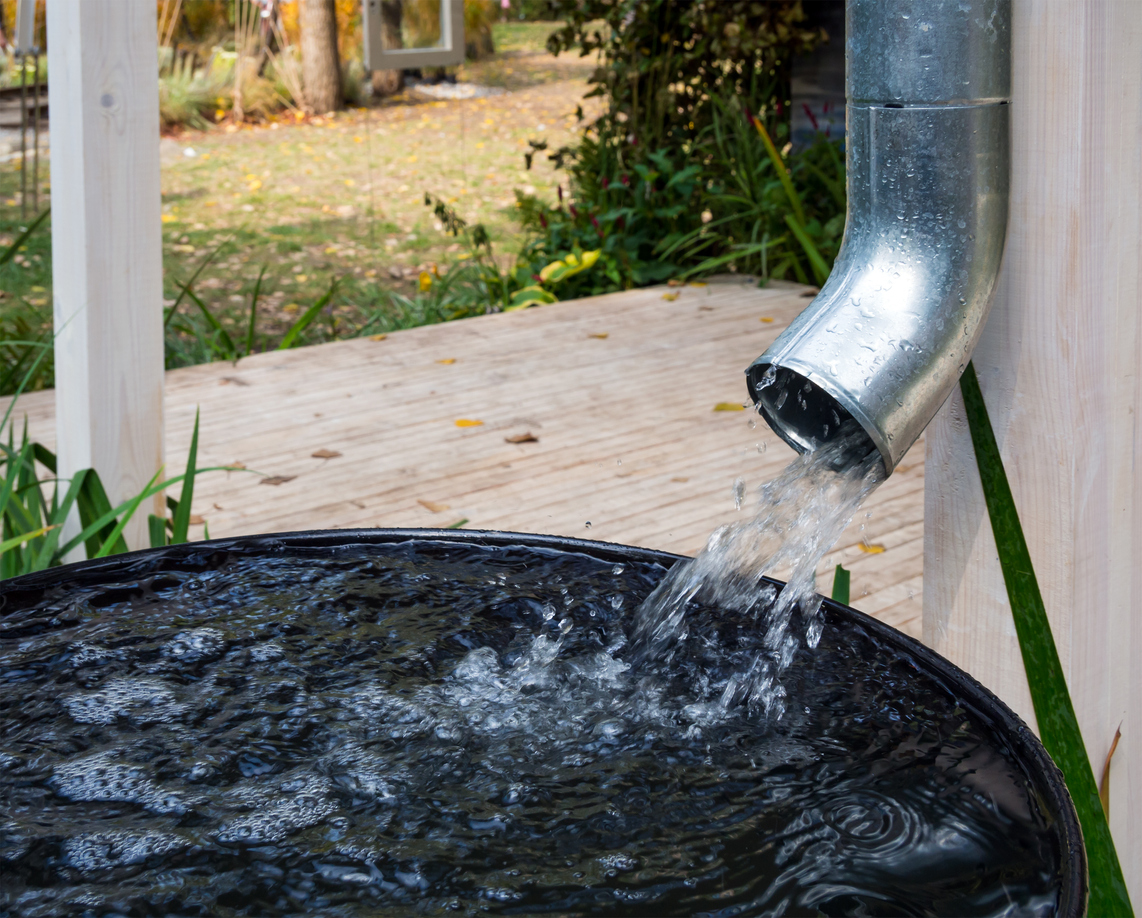

A Beginner’s Step-by-Step Guide to Rainwater Harvesting
Rainwater harvesting is the eco-friendly practice of collecting and storing rainwater for later use. While it might sound complex, it’s quite achievable with these four steps.
Step 1: Assess Your Needs
Start by assessing how much water you use to calculate how much rainwater you must collect. Track your water meter readings for a few weeks to see your daily consumption. Remember to consider how factors like seasonal changes and household size impact your water needs, as well as strategies you can implement to reduce water use to promote sustainability.
If the hydration is for your garden, evaluate how much your plants require during different times of year. If you’re looking to supplement your indoor supply, take into account all activities where water is used in the home. This enables you to design a sufficient rain collection system.
Most importantly, estimate the size of the surface to establish how much rainwater you can collect. The general yield rate is 1 inch of rain produces about 0.6 gallons of water per square foot of roof area.
To determine the exact harvesting capacity of your roof:
- Calculate the roof area in square meters by multiplying the length with the width.
- Multiply with your area’s annual rainfall, the yield rate and the runoff coefficient, which measures how efficient your roof is out of 100%. Many use 85% — or 0.85 — to account for some imperfections.
Step 2: Design Your System
Use the information you gather in the first step to select the right collection system. There are several types, each with its advantages and disadvantages.
Here’s a breakdown of the two main types:
| System type | Gravity-Fed Type | Pumped Systems |
| Description | Relies on the natural slope of your land to move water from the catchment area to the storage tank. | A pump is used to move the collected water to the storage tank. |
| Benefits | This system is simple and cost-effective. | Can be used in any setting. |
| Drawbacks | May not work well in flat areas. | Require electricity to run and are more complex to install. |
To choose the best rainwater harvesting method for you, consider your specific needs, the layout of your property and your budget. You also need to designate a storage area for the harvested water.
Storage options include above-ground tanks, barrels or underground cisterns. Tanks are a popular choice for their ease of installation and maintenance. They’re made from various materials — from plastic to concrete and metal — and are available in multiple sizes to suit various needs.
Be mindful of potential contaminants when choosing a place to store the collected rainwater. Drinking contaminated water predisposes you to various health issues, including gastrointestinal and neurological conditions. Plan for proper filtration and routine water treatment to help remove contaminants and guarantee the safety of harvested water.
Step 3: Install the Collection System
With your design in place, installing the whole system is next. For most structures, the roof is the collection area. Its size and shape determine how much water you can collect. A larger, steeper roof will capture more rainwater. Materials like metal and tile are typically the best options because they don’t leach harmful chemicals into the water.
Gutters and downspouts should be installed strategically, directing rainwater from the roof to the storage area. Leaf guards and gutter screens help keep debris out of the system. Invest in first-flush diverters to keep the first flow of rainwater — which often contains the most contaminants — from entering the tank or cistern. Connect the downspouts to the storage area and install overflow pipes to channel excess water to another location.
If you decide to treat your own water, opt for safe treatment options. Over 60% of municipal water services use chlorine to protect against waterborne diseases. You, too, can try using this tried-and-tested solution, but be careful not to add too much. High levels are linked to medical complications like miscarriages and low sperm count.
Step 4: Maintain Your Rainwater Harvesting System
Regular maintenance helps keep your collection system working efficiently:
- Remove fallen leaves, animal droppings and dirt from the gutters and downspouts to maintain optimal water flow.
- Routinely inspect the storage vessel for damage, leaks and algae growth. Fix as necessary.
- To prevent impurities from entering the water, clean filters and screens.
- If you’re using a pump, ensure it’s in good working condition.
Seasonal maintenance is also important. If you live in colder climates, you may have to winterize your system to protect it from snow damage.
Reap the Benefits of Rainwater Harvesting
Collecting rainwater is a practical way to impact your pocket and the environment positively. By following these steps, you can easily set up your own rainwater harvesting system and effectively capture and utilize this valuable natural resource.


Post a comment